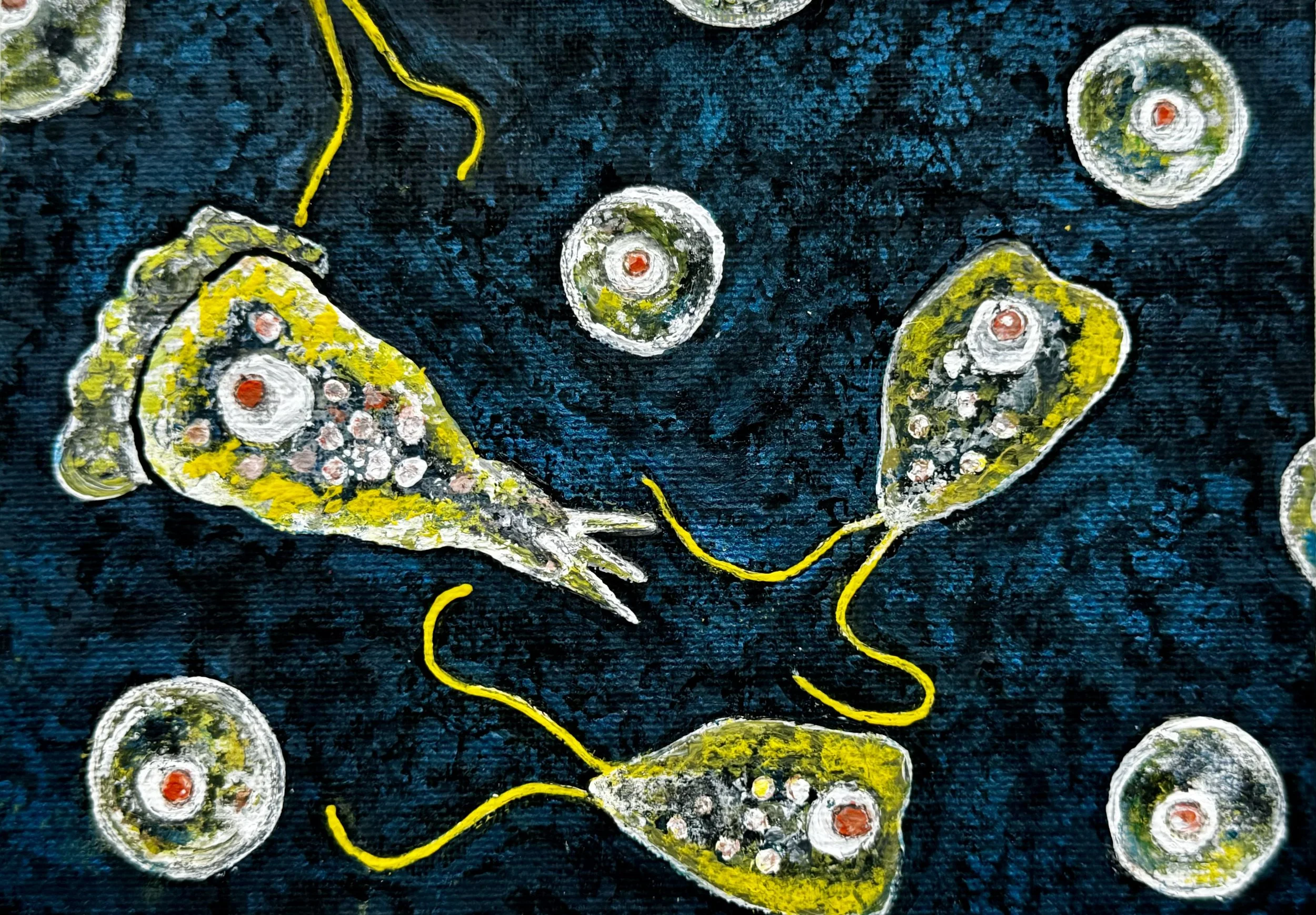
SAFE SUMMER: PREVENT NAEGLERIA FOWLERI INFECTIONNaegleria fowleri in warm freshwater in three life cycle stages (cysts, trophozoites, and flagellated forms); painted by Stephanie Oehler
Naegleria fowleri, commonly referred to as the "brain-eating amoeba," is a rare but deadly single-celled organism found in warm lakes, rivers, or hot springs. The amoeba multiplies at water temperatures around 86º F and thrives above 95º F. Naegleria fowleri enters the nose through contaminated water and then travels to the brain, causing primary amebic meningoencephalitis (PAM). Within 1-9 days after exposure, headache, fever, nausea, vomiting, stiff neck, and confusion typically develop. Symptoms quickly worsen to include seizures, hallucinations, and coma. Unfortunately, the infection is almost always fatal, with a very low survival rate of 3%.
Since PAM is almost always fatal, it is paramount to exercise safe swimming practices during the summer to avoid Naegleria fowleri infection. The best way to prevent infection is to avoid swimming in warm lakes, rivers, ponds, or hot springs during periods of high water temperatures and low water levels. Chlorinated swimming pools are a safer alternative. However, if choosing to swim in freshwater during the summer, keeping your head above water or wearing a nose clip can significantly reduce your risk of exposure. By following these recommended guidelines, you can have an enjoyable but safe summer.